Lyme disease is more widespread than many realize. According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), approximately 300,000 cases of Lyme disease occur annually in the US. The numbers are concerning, and the situation becomes even graver due to the challenge of finding accurate diagnostic tests.
While the disease can be treated, effective management becomes exceedingly difficult without accurate and early diagnosis. Delays in detection can result in severe health issues such as arthritis, heart blockages, and diminished concentration, among others.
Considering the disease’s prevalence and its elusive nature, logical queries arise: What is the most precise Lyme disease test? When should I undergo Lyme disease testing? This article will respond to these and related questions. But first, let’s start with a brief overview.
What Exactly is Lyme Disease?
Lyme disease is an infection triggered by the bacteria Borrelia burgdorferi. This bacterial infection is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected ticks, specifically black-legged ticks or deer ticks. The illness results in symptoms akin to the flu, accompanied by distinctive rashes.
Although the majority of individuals with Lyme disease can achieve full recovery given prompt diagnosis and treatment, certain individuals may experience a recurrence of symptoms in the future. Due to this possibility, it’s crucial to consider testing for Lyme disease even years after the initial infection, particularly if you’ve developed new symptoms following treatment.
When Should I Consider Testing For Lyme Disease?
In areas where ticks are common or if you’ve recently spent time in such regions, it’s advisable to undergo testing for Lyme disease. If you suspect you’ve been bitten by a tick, it’s certainly a good idea to get tested. Reach out to your doctor if you notice any of the early symptoms of Lyme disease, including:
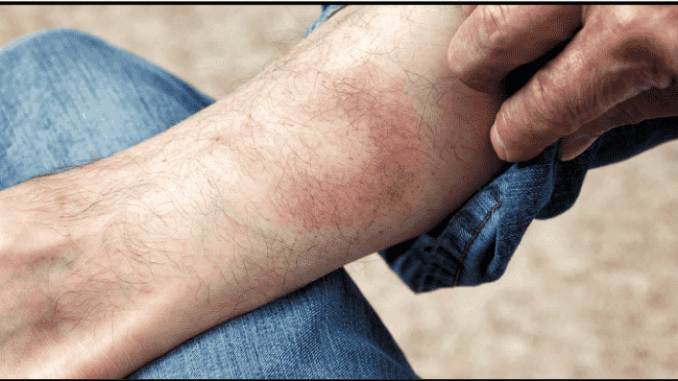
- A rash resembling a bull’s eye at the bite site
- Fatigue
- Muscle aches
- Headaches
- Fever
Certain symptoms might not appear right away. Sometimes, it can take several weeks or even months after the tick bite to notice the following:
- Joint swelling or severe joint pain
- Short-term memory loss
- Facial drooping or loss of muscle tone
- Palpitations or a racing heart
- Nerve pain
- Tingling in the hands and feet
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
While early testing is acceptable, the accuracy of Lyme disease test results tends to improve a few weeks after being bitten by an infected tick. During this time, your body would have generated antibodies, enhancing the test’s ability to detect the disease.
Which Is The Most Accurate Lyme Disease Diagnosis?
Amidst a variety of Lyme disease tests available, pinpointing an accurate diagnosis can be challenging. The disease shares symptoms resembling those of numerous other health conditions, potentially leading to a misdiagnosis of Lyme disease. Compounding this challenge, many available tests for Lyme disease lack precision.
However, the CDC advocates for serological tests, commonly known as blood tests, as the most reliable option for Lyme disease diagnosis. But what sets a blood test apart as the most accurate tool? A serological or blood test functions indirectly.
Rather than directly detecting the Lyme-causing bacteria or their antigens, this test zeroes in on identifying antibodies that the body produces in response to these antigens within an infected individual. If the disease is absent, the body won’t generate antibodies to combat it.
Tests For Lyme Disease
Lyme disease is best tested using two different blood testing methods.
The Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) test
In a nutshell, this test will look for signs that your body is trying to fight off Lyme disease by producing antibodies. However, the ELISA test may come back negative even when a person is infected by the Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria.
False negatives can occur during the early stages of the disease when the infected person’s body has not produced enough antibodies to fight off the B. burgdorferi bacteria. For this reason, reliable diagnosis is not usually based only on the ELISA test results.
Western Blot Test
Let’s break down the Western Blot test in a straightforward manner, without diving into intricate technicalities. Essentially, this test separates the proteins in your blood and identifies antibodies linked to the bacteria responsible for Lyme disease. Typically, if an ELISA test yields a positive result, a Western Blot test is conducted to validate the diagnosis.
For a reliable Lyme disease diagnosis, the CDC suggests the use of standard two-tier testing. Combining the ELISA and Western Blot tests results in a remarkable accuracy rate of 99.9%.
Can Lyme Disease Be Detected Through Blood Test?
A blood test not only detects Lyme disease but is also the most precise and favored method for diagnosing it. In cases where a patient displays indications of Lyme disease affecting the central nervous system, a western blot test can be conducted on the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Treating Lyme Disease
Lyme disease can effectively be treated using antibiotics. If you suspect you’re experiencing Lyme disease symptoms, it’s advisable to undergo testing and receive an early diagnosis. This approach accelerates the recovery process as treatment can be initiated promptly.
Normally, antibiotic treatment for Lyme disease can be delivered orally or intravenously, depending on the disease’s stage. During the initial stages, treating Lyme disease involves administering oral antibiotics over a span of 10 to 21 days, with varying doses based on factors like age, whether the patient is an adult, a breastfeeding mother, or a pregnant woman.
In more severe instances, particularly if the central nervous system is affected, treatment may necessitate intravenous antibiotics for approximately two to four weeks. While the symptoms might not immediately subside, intravenous treatment proves highly effective in eliminating the infection.
Cost Of Lyme Disease Test
The expense associated with a Lyme disease test hinges on the type of test conducted – whether it’s an ELISA test or a combination of ELISA and western blot tests.
On average, an ELISA test for Lyme disease generally costs around $120 or more. If you opt for the additional confirmation provided by a western blot test, the total might go up by $130 or more.
While an ELISA test might yield a negative result, it’s advisable to couple it with a western blot test. This is because not everyone displays the distinct rash or bull’s eye symptoms associated with Lyme disease.
Following a successful diagnosis and treatment, it’s equally important to consider a follow-up Lyme disease test in the years ahead. This helps ensure that any similar flu-like symptoms are attributed to other causes and not a recurrence of the same disease.
Are Lyme Disease Test Kits Accessible?
Indeed, you can find kits for at-home Lyme disease testing that facilitate blood collection. The cost of these kits can range from as low as $20 to potentially $100 or more. Utilizing a Lyme disease test kit is uncomplicated – it involves pricking your finger and then applying or collecting the blood on the provided kit for testing purposes.
However, it’s important to note that while at-home testing kits are available, undergoing Lyme disease testing in a controlled setting like a laboratory or clinic is recommended. Qualified healthcare professionals in such environments are more likely to administer a trustworthy test.
Conclusion
Lyme disease presents a complex challenge that demands early detection and accurate diagnosis. With its wide range of symptoms that can mimic other health issues, seeking timely testing is essential for effective management.
Remember, Lyme disease is not to be underestimated, and a proactive approach to testing and treatment can lead to better outcomes. Stay informed, remain vigilant, and prioritize your health to effectively tackle this intricate ailment.
